ABP (ASP.NET Boilerplate) is a comprehensive, open-source framework for building enterprise applications in .NET.
It offers a modular architecture, reusable components, and a set of tools that facilitate rapid, maintainable, and scalable development.
ABP Framework is a complete infrastructure for creating modern web applications following best practices and conventions for developing enterprise applications, such as inventory management, CRM, ERP, and more.
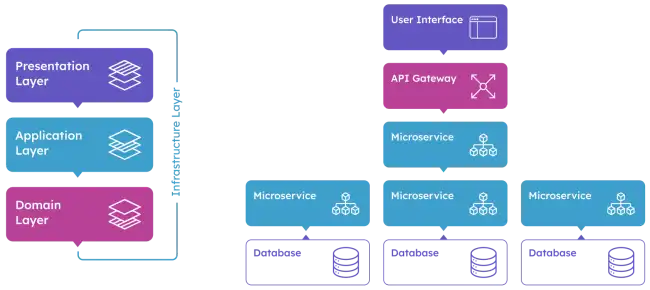
It includes everything needed to develop an application, such as architecture, security, authentication, authorization, error handling, versioning, object-relational mapping, among others.
Features of ABP,
- Modular Architecture: Facilitates organizing code into reusable modules.
- Dependency Injection: Built-in support for dependency injection.
- ORM: Integration with Entity Framework Core and other ORMs.
- Authentication and Authorization: Support for different authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Internationalization: Support for multilingual applications.
- UI: Integration with Blazor, Angular, and other UI frameworks.
- Task Automation: Tools for development and deployment automation.
Installing ABP
Installing the ABP CLI Tool
ABP provides a CLI (Command Line Interface) tool to facilitate project creation and management. You can install it globally using the following command:
dotnet tool install -g Volo.Abp.Cli
Creating a New ABP Project
You can create a new project using the ABP CLI tool:
abp new MyProject -t app
This command creates a new ABP solution with a default project structure and several preconfigured modules.
Initial Configuration
Project Structure
A typical ABP project has the following structure:
- src: Contains the application source code.
- MyProject.Application: Contains the application logic.
- MyProject.Domain: Contains domain entities and business rules.
- MyProject.EntityFrameworkCore: Entity Framework Core configuration.
- MyProject.HttpApi: API controllers.
- MyProject.Web: Web project for the UI.
Database Configuration
ABP uses Entity Framework Core as the default ORM. To configure the database, open the appsettings.json file in the MyProject.DbMigrator project and update the connection string:
“ConnectionStrings”: { “Default”: “Server=(localdb)\mssqllocaldb;Database=MyProjectDb;Trusted_Connection=True” }
Database Migrations
To apply Entity Framework Core migrations, navigate to the MyProject.DbMigrator project directory and run:
dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate dotnet ef database update
Developing Applications with ABP
Creating Domain Entities
Define your domain entities in the MyProject.Domain project. For example, create a Product entity:
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Entities;
public class Product : Entity<Guid>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public Product(Guid id, string name, decimal price)
{
Id = id;
Name = name;
Price = price;
}
}
Repositories
ABP provides generic interfaces for repositories. Create a repository for the Product entity:
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories;
public interface IProductRepository : IRepository<Product, Guid>
{
// Specific methods for the Product entity
}
Application Services
Create application services to handle business logic. For example, a service to manage products:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Volo.Abp.Application.Services;
public class ProductAppService : ApplicationService, IProductAppService
{
private readonly IProductRepository _productRepository;
public ProductAppService(IProductRepository productRepository)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
}
public async Task CreateProductAsync(string name, decimal price)
{
var product = new Product(Guid.NewGuid(), name, price);
await _productRepository.InsertAsync(product);
}
// Other service methods
}
API Controllers
Define API controllers in the MyProject.HttpApi project to expose application services. For example, a controller for products:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
[Route("api/products")]
public class ProductController : MyProjectController
{
private readonly IProductAppService _productAppService;
public ProductController(IProductAppService productAppService)
{
_productAppService = productAppService;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> CreateAsync(CreateProductDto input)
{
await _productAppService.CreateProductAsync(input.Name, input.Price);
return Ok();
}
// Other controller methods
}
UI with Blazor
ABP supports creating user interfaces with Blazor. Create components in the MyProject.Web project to interact with application services.
@page "/products"
@inject IProductAppService ProductAppService
<h3>Products</h3>
<button @onclick="CreateProduct">Create Product</button>
@code {
private async Task CreateProduct()
{
await ProductAppService.CreateProductAsync("New Product", 10.0m);
}
}

