In this tutorial, we are going to see how to create a new Vue application from scratch. Which, logically, is the first step to start working with Vue.
There are two main ways to create a Vue application currently, both are based on Vite (a web development tool).
This is because the Vue team decided that Vite is a more modern and faster option for development, with a great experience for developers.
In this tutorial, we will see both ways, and when it is convenient to use each one.
Before Vue 3, the recommended method for creating a Vue application was using the official tool called Vue CLI. It is no longer used now.
Prerequisites
Before starting, let’s make sure we have the following installed.
- Node.js: Astro runs on Node.js, so you need to have it installed on your system.
- NPM: The package manager included with Node.js
- Code editor or IDE: I recommend using Visual Studio Code.
That is, more or less the usual tools for any web development. But, in case you don’t know some of them, I leave you some links.
Create a new Vue.js application
As I said, there are two main ways to create a Vue application, and both are based on Vite:
Use the official Vue template
The recommended way is to use the official Vue template. It provides a configuration optimized for Vue and a project structure, prepared with the Vue team’s best practices.
To create an application with the official Vue 3 template, we run:
npm create vue@latest
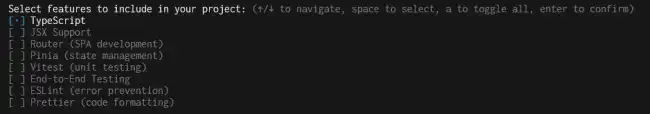
The wizard will ask us a series of questions to configure the project:
- Project name: The project name. For example:
my-vue-app - Add TypeScript? → No (for this tutorial we will work only with JavaScript)
- Add JSX Support? → No
- Add Vue Router for Single Page Application development? → Yes
- Add Pinia for state management? → Yes
- Add Vitest for Unit Testing? → No
- Add End-to-End Testing with Cypress? → No
- Add ESLint for code quality? → Yes
- Add Prettier for code formatting? → Yes
Use the Vite template
The second option is to use the Vite template directly. As we said, Vue uses Vite internally, so we can also create a Vue project by doing.
npm create vite@latest
The wizard will ask us to choose between several frameworks, among which Vue is listed.
- Vue → We select Vue as the framework
- JavaScript or TypeScript → We choose JavaScript for this tutorial
The structure generated by vite is very similar to the official Vue template, but it is less customized for Vue specifically and more oriented towards a minimal configuration environment.
This will create a much lighter and more straightforward Vue configuration, but without Vue Router or Pinia preconfigured. If we need these tools, we must install them manually.
Which option is better?
- ✅ If you want a ready-to-use configuration, with Vue Router, Pinia, and Vue’s best practices, choose
npm create vue@latest. - ✅ If you want a minimal and more customized configuration, or are setting up a mixed architecture, choose
npm create vite@latest(with Vue).
For the course, I will use the official template (npm create vue@latest) because it is more complete and optimized for Vue projects
Run the application
Now that we have our application created, whichever method we chose, let’s see how we can run our application.
When the process finishes, we will see that the project has been created in a directory with the name we provided. First, let’s go to the folder we created with,
cd mi-app-vue
First, we need to install the project dependencies. To do that, we run,
npm install
Now we can launch the application and verify that everything works. We can start the development environment with:
npm run dev
This will start a development server and we can open the application in the browser at the URL http://localhost:5173.
If everything went correctly, you should see a web page with an initial message from our HelloWorld.vue component.
Congratulations! You are ready to start practicing with Vue.Js 🎉.
When you want to distribute your application, we will run,
npm run build
Vite will create the application, and save the result in the dist folder of your project. Ready.
